
How much electricity does an oven use? This is a crucial question for your home budget. Electric ovens generally consume between 2,000 and 5,000 watts of power. The average oven wattage is approximately 3,000 watts. You might ask yourself, how much electricity does this translate to hourly? An electric oven typically consumes around 2 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per hour of use. While a 3,000-watt electric oven running at full power for one hour would consume 3 kWh, ovens do not continuously draw full power. They cycle on and off to maintain the desired temperature. This reduces actual energy usage to approximately 2 kWh per hour. Understanding your oven electricity use is key to managing your household energy bills. Knowing how many watts does an oven use helps you control costs.
Key Takeaways
Electric ovens use about 2,000 to 5,000 watts of power.
Ovens do not use full power all the time; they cycle on and off to keep the right temperature.
You can save money by using smaller appliances like air fryers or microwaves for small meals.
Skipping preheating for some foods and using residual heat can lower your energy bill.
Good oven insulation and choosing energy-efficient models help save electricity.
Oven Electricity Use Explained
Average Oven Wattage
You might wonder about the typical wattage of an electric oven. Most electric ovens draw between 2,000 and 5,000 watts. A common electric oven wattage is around 3,000 watts. However, your oven does not continuously pull this maximum power. Heating elements cycle on and off to maintain the set temperature. This cycling means the actual oven electricity use per hour is often lower than the rated wattage suggests. For example, a 3,000-watt oven operating at high heat would consume 3 kWh per hour if it ran constantly. But because of cycling, the actual consumption is closer to 2 kWh or 2.3 kWh per hour.
Consider this: one user recorded their oven’s energy consumption over 1 hour and 5 minutes. The total was 1.95 kWh. The initial heating phase, which lasted 20 minutes, consumed 1.03 kWh at 3.1–3.2 kW. For the next 45 minutes, the oven cycled to maintain temperature, averaging 1.23 kW. If you extend this to a full two hours of cooking, the total consumption would be approximately 3.07 kWh. A rough estimate for an electric oven’s consumption over an hour, considering the initial high draw (3-3.5 kW for about 15 minutes) and subsequent cycling (averaging 1-1.5 kW), is between 2.5 to 3.0 kWh. You can usually find your specific oven’s wattage in its user manual or on the manufacturer’s website. Knowing how many watts does an oven use helps you understand its energy demands.
Wattage by Oven Type
Different types of ovens have varying wattages. A standard electric oven or an electric stove typically falls within the 2,000 to 5,000-watt range. However, specialized ovens, like convection ovens, have their own power requirements. Convection ovens, sometimes called Air Fryer Toaster Ovens or Countertop Ovens, usually have a minimum wattage of 1400W and a maximum wattage of 1800W. These ovens use fans to circulate hot air, which can sometimes lead to more efficient cooking, but their initial power draw is still significant. Understanding how many watts your specific oven type uses is key to calculating your overall energy usage.
Wattage During Cooking Stages
The oven electricity use changes throughout the cooking process. When you first turn on your oven, it enters a preheating stage. During this time, the heating elements work at full power to quickly reach the desired temperature. This is when your oven draws the most electricity. Once the oven reaches the set temperature, the elements begin to cycle on and off. They only activate when the temperature drops below the set point. This cycling maintains a consistent temperature without continuous high power draw. This is why the average oven power consumption during cooking is lower than the peak wattage.
After you finish cooking and turn off the oven, a cooling fan might operate. This fan helps cool down the oven’s internal components. This cooling fan operation is not considered a ‘standby’ mode. It serves an extra function (cooling down the oven) and is a temporary state. It does not last indefinitely. Similarly, other temporary power consumption states, such as start delay timers or the cooling down phase for ovens, are not classified as ‘standby’ because they are not indefinite. You are not using energy for cooking, but the oven still performs a necessary function.
How Much Electricity Ovens Use: A Wattage Guide

Watts to kWh Conversion
You need to understand how to convert watts to kilowatt-hours (kWh). This helps you calculate your electric bill. The formula is simple: kWh = W/1000. This means 1 kWh equals 1000 watts used for one hour. For example, a 1000-watt electric appliance running for one hour uses 1 kWh. This conversion shows you how much electricity you consume.
Hourly Oven Energy Usage
Different ovens use varying amounts of power each hour. A microwave oven uses between 600 and 1700 watts. A toaster oven typically draws 1000 to 1500 watts. Convection ovens can use up to 5000 watts. An average modern electric oven uses about 2400 watts on medium to high heat. A typical electric oven’s wattage ranges from 750 to 3,000 watts. For standard use, it averages 1,000 watts. This tells you how many watts does an oven use depending on its type. Knowing how many watts helps you estimate your hourly oven energy usage. You might wonder how much electricity an oven uses hourly. An electric stove or oven’s hourly consumption depends on its wattage and how long it runs.
Monthly and Yearly Consumption
You can estimate your daily power usage. It can range from 750 to 6,000 watt-hours. If you use your oven for one hour daily at 2 kWh, that is 60 kWh per month. Over a year, this adds up. Your yearly kWh of electricity for the oven would be 730 kWh (2 kWh x 365 days). This shows how much electricity an oven uses over time. Understanding this oven electricity use helps you manage your overall energy usage. Knowing how many watts does an oven use for these longer periods helps you budget.
Cost to Power an Oven
Calculating Hourly Operating Costs
You want to know the exact cost to power an oven. Calculating your oven’s hourly operating cost helps you understand your energy bill. First, find your oven’s wattage. You can usually find this on the appliance’s nameplate or in its manual.
Here is how you calculate the hourly operating cost:
Convert wattage to kilowatts: Divide your oven’s wattage by 1000. For example, a 2400-watt oven becomes 2.4 kilowatts (kW).
Calculate kilowatt-hours (kWh) used: Multiply the kilowatts by the hours you use the oven. Remember, ovens cycle on and off. Estimate the actual time the heating element is active.
Determine the cost per kWh: Look at your electricity bill. Divide the total current charge by your kWh usage for that period. The average residential electricity rate in the U.S. is about 17.47 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
Calculate the operating cost: Multiply the kWh your oven uses by your cost per kWh.
For instance, an oven using 2400 watts for one hour a day at a cost of $0.10 per kWh would cost $0.24 for that hour. This simple calculation shows you the cost to run an oven for a specific period.
Factors Affecting Your Oven Bill
Several factors influence the cost of powering an oven. Understanding these helps you manage your energy consumption.
Usage Duration and Frequency: The longer you use your oven, the more electricity it consumes. Frequent use of high-temperature settings significantly increases your energy bills. Skilled cooks know that most electric ovens are robust appliances that consume a lot of electricity.
Temperature Settings: Your chosen temperature affects consumption. Using a convection setting can reduce energy consumption by up to 20% compared to the bake setting. You can also lower the oven temperature by about 25 degrees Fahrenheit when baking with ceramic or glass pots and pans. This impacts how much electricity your oven uses.
Oven Insulation: Good insulation is key to reducing energy costs. Insulation decreases heat dissipation. It improves oven efficiency by ensuring uniform heat distribution. It also prevents heat transfer to your oven’s exterior. Thicker insulation directly reduces energy loss through oven walls. This leads to significant cost savings. Inspecting and replacing degraded insulation in older ovens can boost efficiency. It also enhances worker safety by minimizing burn risks. A well-insulated oven reaches a steady temperature faster. It also maintains that temperature with less energy.
Comparing Oven Types for Efficiency
When considering the cost to run an oven, comparing different types for their energy efficiency is important.
Oven Type | Efficiency Rating |
|---|---|
Gas | 40% |
Electric (radiant) | 75-80% |
Induction | 85% |
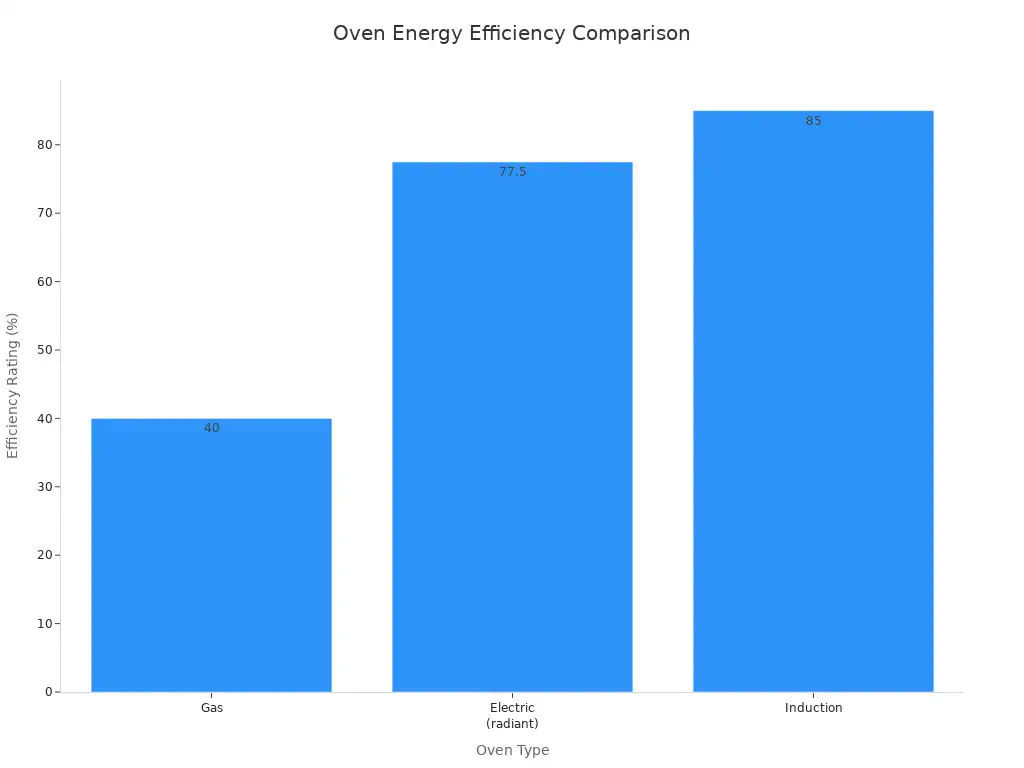
Gas ovens are less efficient. Only 40% of the energy from burning gas reaches your food. This is due to significant heat loss during combustion. In contrast, electric radiant ovens achieve 75-80% efficiency. Induction ranges are the most efficient at 85%. They directly heat cookware through magnetic induction. This minimizes energy loss.
True convection ovens are more energy efficient than most conventional ovens. They cook food faster. This requires less energy overall. They also do not need to heat up as much during preheating. This further reduces energy consumption. An ENERGY STAR certified electric stove or convection oven offers even greater savings. For example, ENERGY STAR certified commercial convection ovens are approximately 27% more energy efficient than standard models. An ENERGY STAR certified electric convection oven saves businesses about $150 annually. It saves $1,300 over its lifetime compared to standard models. It also saves approximately 1,200 kWh annually. This shows the significant impact of energy efficiency on the cost of powering an oven.
Reducing Oven Energy Usage

You can significantly lower your electricity bill by adopting smarter cooking habits. Understanding your oven energy usage helps you make informed choices.
Smart Cooking Habits
You can save energy by changing how you use your oven. Preheating your oven is not always necessary. A 1982 study showed that skipping preheating for all tested food items saved up to 10% energy during cooking. It also reduced cooking time by five minutes or more. Experts like Andrea Schneiker and Jens Behrend from Dr. Oetker confirm that many frozen pizzas and baking mixes do not need preheating. This may extend cooking time slightly, but it saves energy. Always check your food’s doneness, as cooking times can vary.
You can also use residual heat effectively.
Cooking on an electric range creates residual heat. This heat stays after you turn off the burner.
You can save energy by using this heat.
Turn off the burner a few minutes before your food finishes cooking.
The remaining heat will continue to cook your food without using more electricity.
This method works well for dishes that need simmering or steaming.
Maximizing Oven Efficiency
Maintaining your oven helps improve its energy efficiency. A well-maintained oven heats up faster. It also spreads heat more evenly. This saves energy. It also reduces the risk of problems. Keeping your oven clean stops old food and grease from building up. This can affect your food’s taste and even cause a fire.
Self-cleaning ovens are more energy efficient because they have better insulation.
You save on energy costs with a self-cleaning oven in two ways. First, they handle high temperatures. This means they are built well. They have very good insulation. This insulation keeps heat from escaping. Only ovens with high energy efficiency can do this.
Alternative Cooking Methods
Consider using smaller appliances for smaller meals. This is a key step in reducing your oven’s electricity usage. Using a microwave oven for small amounts of food can cut energy costs by up to 80%. This is compared to using a full-sized conventional oven. The federal government’s Energy Star program supports this data.
Toaster ovens also offer energy savings. They heat up quickly. They use less energy than traditional ovens.
Air fryers are another great option. Food cooks 25% faster in an air fryer than in an oven. This reduces both cooking time and electricity usage. A recent study showed a family cut their kitchen’s cooking energy use by nearly 40%. They used an air fryer for most oven meals. This was due to shorter cook times and less preheating.
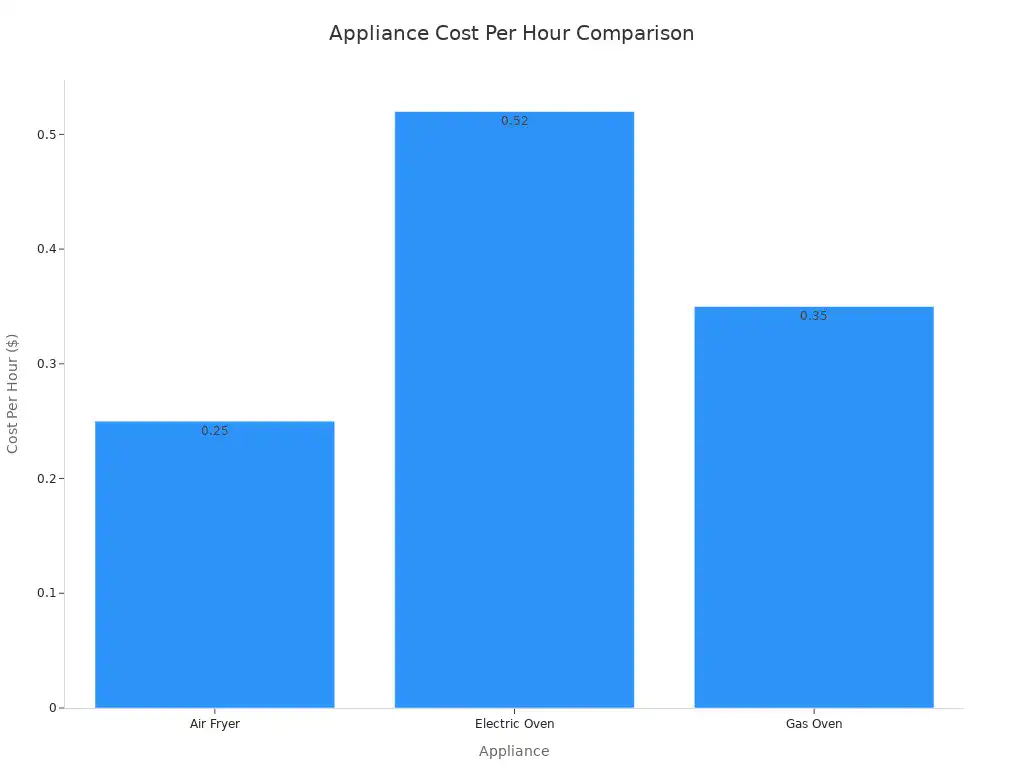
Appliance | Wattage Range | Cost Per Hour |
|---|---|---|
Air Fryer | 1,000 – 1,800 W | $0.25 |
Electric Oven | 2,500 – 5,000 W | $0.52 |
Gas Oven | N/A | $0.30 – $0.40 |
Air fryers cook up to twice as fast as an average oven.
Air fryers do not need preheating. Ovens take 10-15 minutes to preheat.
You now understand your oven electricity use, including average wattage and cost. Knowing how much power your electric oven draws is crucial for managing your household budget. You learned about different oven types and their efficiency. Implement smart cooking habits, maximize your electric oven’s efficiency, and consider alternative cooking methods. These strategies help you create a more energy-efficient kitchen. Mindful energy consumption benefits both your finances and the environment.
FAQ
How much electricity does an oven use per hour?
An electric oven typically uses about 2 to 2.3 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per hour. This is because the heating elements cycle on and off. They do not run at full power constantly. This cycling helps maintain your set temperature.
Why does my oven’s actual usage differ from its rated wattage?
Your oven’s rated wattage shows its maximum power draw. However, it does not continuously pull this power. The heating elements cycle on and off to maintain temperature. This means the actual energy consumption is lower than the maximum rating.
What is the average cost to run an oven?
The cost to run an oven depends on your electricity rate and how long you use it. If your oven uses 2 kWh per hour and electricity costs $0.15 per kWh, it costs $0.30 per hour. You can calculate your specific cost using your bill.
Does preheating always save energy?
No, preheating does not always save energy. For many dishes, like frozen pizzas, you can skip preheating. This saves energy. Always check your food’s instructions. You can also use residual heat by turning off the oven early.

