
You find ozone generators appealing for removing tough odors and purifying air. However, you must understand ozone’s powerful oxidizing nature. This makes safety critically important. Proper ventilation and the complete absence of people and pets during operation are non-negotiable. This guide provides comprehensive steps for safe and effective home use of an ozone generator.
Key Takeaways
Ozone generators make ozone gas. This gas removes bad smells by changing odor molecules. Ozone is a strong chemical.
Never use an ozone generator when people, pets, or plants are in the room. Ozone can harm living things, especially your lungs.
Always air out the room well after using an ozone generator. Open windows and use fans to remove all ozone gas.
Ozone can damage things like rubber, plastics, and some fabrics. Remove or cover sensitive items before you use the generator.
Many health groups warn against using ozone in homes. They say it is safer to use air purifiers with filters instead.
What Is An Ozone Generator

You might wonder what an ozone generator actually does. It is a device that creates ozone gas. Understanding ozone itself helps you grasp how these machines work.
Understanding Ozone (O3)
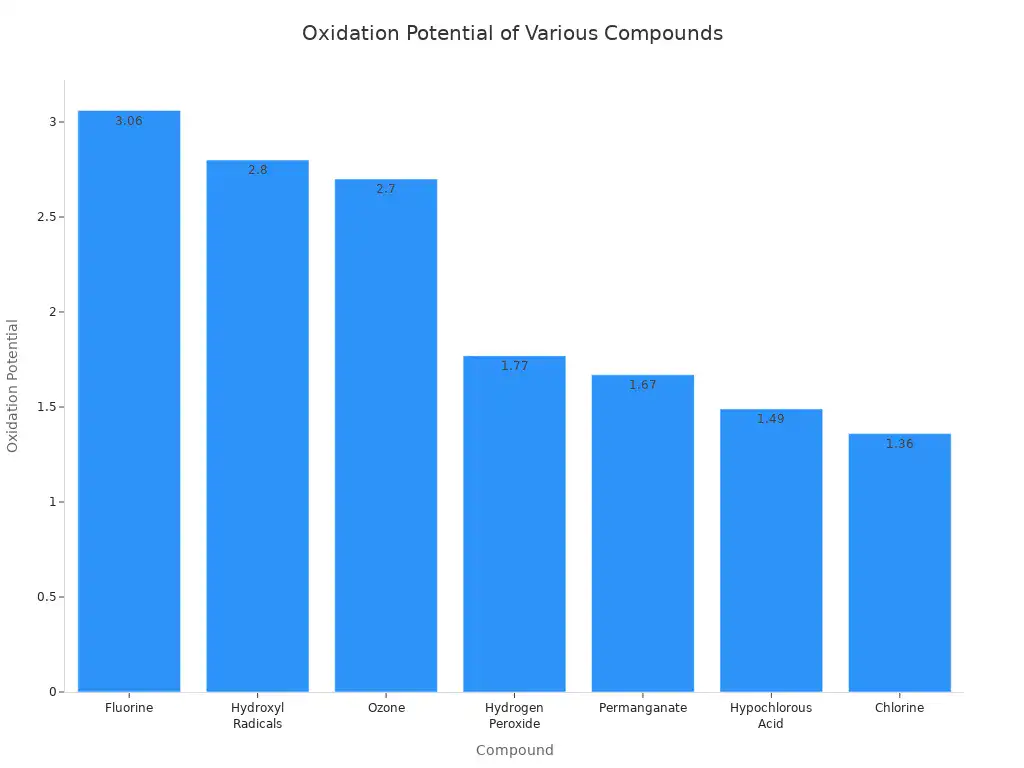
Ozone is a molecule made of three oxygen atoms (O3). Regular oxygen, the air you breathe, has two oxygen atoms (O2). That extra atom makes ozone very reactive. It is a powerful oxidizer. Look at this table showing oxidation potential:
Compound | Oxidation Potential |
|---|---|
Fluorine | 3.06 |
Hydroxyl Radicals | 2.80 |
Ozone | 2.70 |
Hydrogen Peroxide | 1.77 |
Permanganate | 1.67 |
Hypochlorous Acid | 1.49 |
Chlorine | 1.36 |
As you can see, ozone has a high oxidation potential. It ranks third after fluorine and hydroxyl radicals. This means ozone readily gives up one of its oxygen atoms. This process changes other molecules it contacts. Ozone is also unstable. It naturally breaks down into regular oxygen over time.
How Ozone Neutralizes Odors
Ozone neutralizes odors through a chemical reaction called oxidation. The third oxygen atom in ozone is very eager to react. When ozone meets odor-causing substances, it transfers this extra oxygen atom. This changes the odor molecule’s chemical structure.
For example, ozone reacts with:
Bacteria
Smoke particles
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
This reaction breaks down the compounds. They turn into substances that do not smell. This process effectively removes unpleasant odors from the air.
Ozone Generators Versus Air Purifiers
An Ozone Generator creates ozone gas. It does this by splitting oxygen molecules into single atoms. These atoms then combine to form O3. The ozone gas then reacts with pollutants in the air. This changes their chemical makeup.
Air purifiers work differently. They use physical filtration. HEPA filters, for instance, trap airborne particles. These include dust, pollen, and pet dander. Activated carbon filters can capture gaseous contaminants. Air purifiers remove pollutants from the air. They do not release new substances into your home. Ozone generators, however, intentionally release a reactive gas. This gas can be harmful.
Ozone Generator Safety Precautions
You must understand the serious risks before you use an ozone generator. Your safety and the safety of others depend on following strict rules.
Never Operate In Occupied Spaces
You must ensure no one is in the area when an ozone generator runs. This includes all humans, pets, and even plants. Ozone is a powerful gas. It can harm living things.
Exposure to ozone, even for a short time, can cause immediate health problems. You might experience:
Lung Function Decrements: Your lungs may not work as well. You might find it hard to take a deep breath.
Respiratory Symptoms: You could cough, have a sore throat, or feel chest pain when you breathe deeply. Your chest might feel tight. You could also wheeze or feel short of breath.
Airway Inflammation: The inside of your airways can become red and swollen. This shows cell damage.
These effects usually go away within a few hours or up to two days after exposure stops. However, you must avoid them completely. Pets and plants are also very sensitive to ozone. You must remove them from the treatment area.
Ventilation Is Key
Good ventilation is crucial. You need to air out the treated space thoroughly after using an ozone generator. This helps remove any remaining ozone gas. You will learn more about post-treatment ventilation later. Remember, proper airflow helps clear the air.
Understanding Ozone Levels
You might hear about “safe” ozone levels. However, these levels are often misleading for home use. Government agencies set limits for workplaces. These limits show how dangerous even small amounts of ozone can be over time.
For example, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets workplace limits.
Category | Limit |
|---|---|
PEL-STEL | 0.30 ppm (0.60 mg/m³) |
REL-C | 0.1 ppm (0.2 mg/m³) |
OSHA’s permissible exposure limit (PEL) for ozone is 0.1 part of ozone per million parts of air. This is an average over an eight-hour workday. This means you should not breathe air with more than 0.10 ppm of ozone for 8 hours a day. Even lower levels are recommended for moderate or heavy work.
Residential ozone generators can produce much higher ozone concentrations. They often increase indoor ozone levels to well above these health standards. You might see levels over 100 parts per billion (ppb), sometimes as high as 650 ppb. Peak ozone concentrations can reach 100 to 450 ppb. These levels are far above what OSHA considers safe for continuous exposure.
When you breathe ozone, it causes specific changes in your body:
Ozone makes your airways inflamed and overly reactive.
It reacts with fats in your lung lining. This creates harmful products.
These products act as signals. They start a chain reaction in your cells.
This chain reaction activates pathways that cause inflammation.
Your body then produces inflammatory chemicals.
Long-term ozone exposure causes stress to your cells. This can damage your breathing system. It can also harm other organs like your skin, liver, heart, kidneys, and brain.
Your lungs have limited protection against ozone. This makes the harmful effects worse.
Therefore, you must never be in the room when an ozone generator is running. Even low levels of ozone can cause harm over time.
Personal Protective Equipment
You do not need personal protective equipment (PPE) during the operation of an ozone generator. This is because you must not be in the treated space at all. After treatment, you will ventilate the area. You should wait until the ozone has cleared before re-entering. If you must enter the area briefly before full ventilation, you might consider a respirator designed for ozone. However, the best practice is to wait until the air is completely clear.
How To Use Ozone Generators Safely

You must follow specific steps to use an ozone generator safely and effectively. These steps protect you and your home.
Preparing The Area
You must prepare the area carefully before you start the ozone treatment. First, remove all living things. This means all people, pets, and plants must leave the room. Next, remove sensitive items. Ozone can damage certain materials.
Take out any artwork, plants, and electronic devices. If you cannot remove large items, cover them well. You might need to seal off the treatment area. Close all doors and windows. This keeps the ozone inside the room.
Optimal Unit Placement
Place your ozone generator in the best spot for good results. Ozone is heavier than air. It tends to settle near the floor. For even air distribution, place the unit higher up. A wall-mounted ozone generator works best at about 1.8 to 2.2 meters (6 to 7.2 feet) above the ground. This helps the ozone mix well with the air. You should also plug the unit into an outlet near the entry door. This lets you unplug it quickly and safely from outside the room.
Setting The Run Time
You need to set the correct run time for your ozone generator. This depends on the room size and how strong the odors are.
Measure the Room Volume: First, find the room’s volume. Multiply its length by its width by its height. If the room has an odd shape, divide it into smaller sections. Then add their volumes together.
Consider Odor Intensity: The stronger the smell, the longer the treatment time.
Space Type | Odor Intensity | Treatment Time |
|---|---|---|
Homes and Apartments | Mild | A few hours |
Homes and Apartments | Moderate | 4–6 hours |
Homes and Apartments | Severe | 8–12 hours or overnight |
Cars | Odor removal | 4–10 minutes (frequent) |
Offices and Commercial Buildings | Standard office | 30 minutes to 2 hours |
Offices and Commercial Buildings | Smaller spaces | 15–30 minutes |
Offices and Commercial Buildings | Open floor plans | 1–2 hours |
Heavily contaminated spaces | Severe contamination | Extended treatment times |
Heavily contaminated spaces need longer times. Ozone reacts with pollutants first. It needs time to reach full disinfection levels. You can also use a fan during treatment. A fan helps spread the ozone around the room. This makes the treatment more effective.
Post-Treatment Ventilation
After the ozone generator finishes its cycle, you must ventilate the area. This step is very important. Open all windows and doors. Use fans to move fresh air into and out of the room.
For small spaces like homes or offices, ventilate for at least 30 minutes to 1 hour.
If you used high ozone concentrations or treated a large area, ventilate for 1 to 2 hours or even longer.
For very high concentrations or poor ventilation, extend this to 2 to 3 hours.
The goal is to remove all remaining ozone gas.
Safe Re-Entry
Do not re-enter the treated space too soon. You must allow enough time for the ozone to break down.
Wait: After the ozone machine stops, wait at least two to four hours. For very high ozone levels or large rooms, you might need to wait up to 24 hours. This gives the ozone time to dissipate.
Ventilate: After waiting, make sure you have ventilated the area well. Open windows and use fans.
Check for Safety: Do not rely only on your nose. The absence of a strong ozone smell does not mean the air is safe. Use an ozone detector to check the air quality. Make sure ozone levels are below the safe exposure limit of 0.05 ppm.
Watch for Symptoms: If you re-enter and feel any symptoms like coughing or throat irritation, leave the area right away. Seek medical help if needed. Your safety is the top priority.
Ozone Generator Applications And Benefits
You understand the safety rules. Now, you can learn about the benefits of using an ozone generator. These devices offer powerful solutions for specific problems in your home.
Effective Odor Removal
You can use ozone to eliminate many strong, persistent odors. Ozone generators are very effective against tough smells. These include food odors, smoke odors, and pet odors. They also tackle cigarette and marijuana smells. You can remove mold and mildew odors too. Ozone molecules interact with volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These compounds cause many bad smells, especially from smoke. Ozone breaks down these VOCs into substances that do not smell. This process effectively removes unpleasant odors from the air.
Addressing Bacteria And Viruses
Ozone gas is also effective against many bacteria and viruses. It can inactivate them on surfaces. Ozone shows strong bactericidal properties. It works even against multidrug-resistant bacteria. It also has virucidal efficacy. This means it can kill many viruses. These include SARS-CoV-2, influenza A, and norovirus. The effectiveness of ozone depends on a few things. These include its concentration, how long it is exposed, and the humidity. Higher humidity often helps ozone work better. It creates more free radicals. Ozone works well at different temperatures. It can even work in refrigerated areas.
Specific Use Cases
You can use ozone generators in many specific situations. They are great for removing smells from used cars. This eliminates odors from previous owners, like smoke or pets. You can use them after smoke damage from cigarettes or small fires. They help with heavily contaminated vehicles, like taxis. These vehicles often have deep-seated smells. Family cars with frequent spills also benefit. Ozone tackles cigarette smoke and pet odors. It removes food spills and drink stains. It also eliminates mold and mildew smells from moisture. You can use it for odors from vomit, blood, urine, feces, and body odor.
Ozone Risks And Misconceptions
You must understand the risks and common misunderstandings about ozone. This helps you make safe choices for your home.
Health Hazards Of Exposure
Ozone is not harmless. Breathing ozone, even at low levels, can cause serious health problems. You might experience:
Worsened asthma or other breathing issues.
Increased risk of respiratory infections.
Shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing.
Chest pain and throat irritation.
Long-term exposure to ozone can have lasting effects. It can:
Aggravate asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema.
Reduce lung function in children as they grow.
Lead to adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including a higher risk of death.
Increase your risk of respiratory illnesses, metabolic disorders, and nervous system issues.
Cause reproductive problems, affecting fertility and birth outcomes.
Increase the risk of premature death for older adults, even at levels below current national standards.
Health problems from ozone can continue long after you stop being exposed.
Damage To Materials
Ozone does not just harm living things. It can also damage many materials in your home.
Paints and Coatings: Automobile finishes, latex paints, and oil-based house paints can suffer damage. Paint films with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are very sensitive.
Dyes and Inks: Blue anthraquinone dyes on nylon and acetates can fade. This is known as ‘Gulf Coast Fading’.
Polymers: Natural rubbers crack easily when exposed to ozone. Materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC can also break down. Linear polyurethanes lose strength.
Other Items: Cotton muslin, lamb’s wool, neoprene, plywood, and linen react to ozone. Even electrical components like metal thin films and graphite electrodes can get damaged.
Ozone As “Fresh Air” Myth
Some people think ozone smells like “fresh air” or “clean air.” This is a dangerous misconception. The smell you notice is ozone itself. It is a sign that a harmful gas is present. You should never associate the smell of ozone with cleanliness or health. It means you are breathing a lung irritant.
Health Organization Warnings
Many health organizations warn against using ozone in homes. They highlight the dangers.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets a maximum ozone level of 0.05 ppm for enclosed spaces. This includes homes and offices.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has taken action against companies making false claims about ozone generators.
The Vermont Department of Health suggests choosing other air purification methods. This helps reduce ozone levels indoors.
Important Note: Ozone, even at low levels, irritates your respiratory system. It can worsen asthma and may even cause permanent lung damage. Vulnerable people, like children, the elderly, and those with breathing problems, are especially at risk. These organizations strongly advise against using ozone in spaces where people or animals are present.
Ozone Generator Maintenance
You need to keep your ozone generator in good shape. Proper maintenance ensures it works well and lasts longer.
Cleaning The Unit
You must clean your ozone generator regularly. This keeps it working efficiently. You should clean the plates or filters every three to six months. If you use the unit daily, clean it every four to five weeks. For monthly use, cleaning once a year might be enough.
To clean, use a soft, dry cloth or a brush. For a deeper clean, you can use a mild soap solution. Some parts, like filters, you can wash with detergent, vinegar, or bleach. Scrub them with a brush. Rinse them thoroughly with hot water. Then, dry them completely. You can even use a hairdryer to speed up drying.
Proper Storage
Store your ozone generator correctly when you are not using it. Keep it in a cool, dry place. Protect it from dust and moisture. A clean, covered container works well. This prevents damage to its internal parts.
Troubleshooting Issues
Sometimes, your ozone generator might not produce ozone. You can check a few things if this happens.
Power Supply: First, check the power supply. Make sure the unit is plugged in correctly. Look for any loose connections.
Ozone Switch: Ensure you have turned on the ozone switch.
Blockages: Check for dirt or blockages in the condenser or filter. Clean or replace them if they are dirty.
Water Accumulation: Sometimes, water can build up inside the unit. Dry any accumulated water. Make sure your air source is dry.
Damaged Parts: If these steps do not work, a part might be damaged. This could be the ozone generation module or a fuse. You might need to replace these parts. If you are unsure, contact the manufacturer for help.
You can solve many common problems with these simple checks.
You now know that an Ozone Generator offers powerful solutions for tough odors. However, its use demands strict safety. Always ensure no people, pets, or plants are in the treated area. Ventilate thoroughly after each use. Understand the risks involved. Prioritize your safety above all else. If you feel unsure about using an ozone generator safely, consider professional services or other purification methods.

